Chemistry
quarta-feira, 23 de maio de 2012
quarta-feira, 28 de março de 2012
Science Fair Ideas
- Does coloring carbonated water change how its taste is perceived?
- Do different types of carbonated sodas have different pH?
- Can you tell different brands of soda pop apart based on taste?
- Do some plants grow better inside than outside?
- Which type of water contains the lowest amount of chlorine?
- What type of insulation holds in heat the best?
- Do different types of knots affect the breaking strength of a rope?
- Does wiping a doorknob with an antibacterial wipe really reduce the numbers of bacteria? Does using hand sanitizer really reduce the amount of bacteria on your hands?
- How do different flame retardants affect the flammability and burning rate of cotton?
- Which cooking method results in the least loss of vitamin C?
- Does temperature affect the maximum size you can inflate a balloon?
- Do the color of a crayon affect how long of a line it will write?
- Does changing the temperature affect how long a pen will last?
- Do all types of bread mold at the same rate?
domingo, 29 de janeiro de 2012
Chemistry
What is Chemistry?

Chemistry is the study of matter and energy and the interactions between them. This is also the definition for physics. Chemistry and physics are specializations of physical science. Chemistry tends to focus on the properties of substances and the interactions between different types of matter, particularly reactions that involve electrons.
What do Scientiscs think is made of chemistry?
Everything you hear, see, smell, taste, and touch involves chemistry and chemicals (matter). In more formal terms chemistry is the study of matter and the changes it can undergo. Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. Which is to say, anything you can touch or hold. Common usage might have us believe that ‘chemicals’ are just those substances in laboratories or something that is not a natural substance. Far from it, chemists believe that everything is made of chemicals. Chemistry is not limited to beakers and laboratories. It is all around us, and the better we know chemistry, the better we know our world.
States of Matter
Gases, liquids and solids are all made up of microscopic particles, but the behaviors of these particles differ in the three phases. The following figure illustrates the microscopic differences.
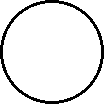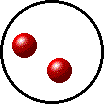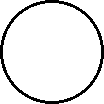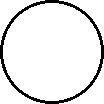 |  | 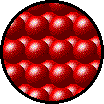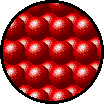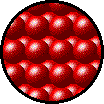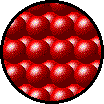 |
Microscopic view of a gas.
|
Microscopic view of a liquid.
|
Microscopic view of a solid.
|
Note that:
- Particles in a:
- gas are well separated with no regular arrangement.
- liquid are close together with no regular arrangement.
- solid are tightly packed, usually in a regular pattern.
- Particles in a:
- gas vibrate and move freely at high speeds.
- liquid vibrate, move about, and slide past each other.
- solid vibrate but generally do not move from place to place.
The following table summarizes properties of gases, liquids, and solids and identifies the microscopic behavior responsible for each property.
Some Characteristics of Gases, Liquids and Solids and the Microscopic Explanation for the Behavior
| ||
|---|---|---|
gas
|
liquid
|
solid
|
assumes the shape and volume of its container
particles can move past one another
|
assumes the shape of the part of the container which it occupies
particles can move/slide past one another
|
retains a fixed volume and shape
rigid - particles locked into place
|
compressible
lots of free space between particles
|
not easily compressible
little free space between particles
|
not easily compressible
little free space between particles
|
flows easily
particles can move past one another
|
flows easily
particles can move/slide past one another
|
does not flow easily
rigid - particles cannot move/slide past one another
|
The three states of Matter Diagram

Solutions
Solutions are groups of molecules that are mixed up in a completely even distribution.This means that they are homogenous system.Other types of mixtures can have a little higher concentration on one side of the liquid when compared to the other side. So, they are heterogenous.
Can Anything Be In Solution?
Solutions can be solids dissolved in liquids. They could also be gases dissolved in liquids. There can also be gases in other gases and liquids in liquids. If you mix things up and they stay at an even distribution, it is a solution.
A simple solution is basically two substances that are going to be combined. One of them is called the solute. A solute is the substance to be dissolved . The other is a solvent. The one that is going to do the dissolving.
Can Anything Change Solutions?
All sorts of things can change the concentrations of substances in solution.
Solubility is the ability of the solvent to dissolve the solute . Some things like temperature, pressure and structure of substance can modify it's solubility .
Sugar dissolves easily in water; oil does not. Water has a low solubility when it comes to oil.
 Only a finite amount of solid will dissolve in a liquid and this is dependent on the solid and the temperature. When no more solid will dissolve the solution is saturated, but generally more will dissolve in hot than in cold liquid and it will dissolve faster if you stir the solution.
Only a finite amount of solid will dissolve in a liquid and this is dependent on the solid and the temperature. When no more solid will dissolve the solution is saturated, but generally more will dissolve in hot than in cold liquid and it will dissolve faster if you stir the solution.
People often confuse melting and dissolving and this may be a point of discussion. Melting requires heat and dissolving requires a solvent. In making a jelly both are happening when it is added to hot water.
SATURATED SOLUTIONS
 Only a finite amount of solid will dissolve in a liquid and this is dependent on the solid and the temperature. When no more solid will dissolve the solution is saturated, but generally more will dissolve in hot than in cold liquid and it will dissolve faster if you stir the solution.
Only a finite amount of solid will dissolve in a liquid and this is dependent on the solid and the temperature. When no more solid will dissolve the solution is saturated, but generally more will dissolve in hot than in cold liquid and it will dissolve faster if you stir the solution.
So if a saturated solution of sugar is made using hot water, as it cools some of the sugar comes out of solution and reforms making crystals. This principle is used to grow crystals. Crystals can also, of course, be made by leaving a salt or sugar solution and allowing the water to evaporate leaving salt or sugar crystals behind.
What is a mixture?
Mixing materials together forms a mixture where two or more substances are physically but not chemically combined and can be separated again by physical methods such as sieving, filtering, evaporating etc. This means that the change can be reversed. A new material is not formed as it is in a chemical reaction. Mixtures can be made up of
- solid in solid (muesli)
- gas in solid (pumice stone)
- solid in gas (smoke)
- gas in gas (air – mostly made up of nitrogen and oxygen)
- liquid in gas (clouds, mist, aerosol)
- gas in liquid (oxygen in water)
- liquid in liquid (emulsion – milk)
- insoluble solid in liquid (suspension – muddy water)
- soluble solid in liquid (solution – salt water).
A mixture is an impure substance that can be separated into pure substance by physical means. eg. dirty water can be purified by filtration.
There are many different methods of separating mixtures. Each method relies on differences in the physical properties of the components of the mixture.
Methods of Physical Separation
| Method of separation | Used to separate | Basis - differences in | Example |
| Filtration | An insoluble solid from a liquid | Solubility | Muddy water |
| Decanting | An insoluble solid from a liquid | Solubility and density | Water and sand |
| Centrifuging | An insoluble solid from a liquid | Solubility and density | Blood cells from plasma |
| Evaporating | A soluble solid from a liquid | Boiling point | Salt from sea water |
| Distillation | A liquid from a soluble solid | Boiling point | Water from sea water |
| Fractional distillation |
Miscible liquids
(liquids that can be mixed together as one)
| Boiling point | Alcohol from water |
| Separating funnel | Immiscible liquids (liquids that do not mix) | Density and miscibility | Oil and water |
| Paper chromatography | Soluble substances | Retention rates on paper | Food coloring |
| Crystallization | Soluble substances | Solublility | Different salts |
Filtration Distillation
What is a pure substance?
A pure substance is a substance that cannot be separated by physical means. eg. filtration, evaporation, distillation or chromatography.- What is pure Water?

 Acid: A solution that has an excess of H+ ions. It comes from the Latin word acidus that means "sharp" or "sour".
Acid: A solution that has an excess of H+ ions. It comes from the Latin word acidus that means "sharp" or "sour".
Alkali: A solution that has an excess of OH- ions. It comes from arabic word ´al kali´that means ashes used by Arabic scientist mixed with water and animal fats to make the first soup.Alkali describe a group of substances that feel soapy.However, many alkalis are too dangerous to feel.
This group include,for example:
- Soap


What is a chemical indicator?

A chemical indicator is a substance that changes color in the presence of an acid and an alkali
Chemical indicators are a safer way to determine if a chemical substance is acidic or basic.
| Chemical indicator | Color in acid | Color in base |
| Litmus paper | Pink /Red | Blue |
| Phenolphthalein | Colorless | Pink/ violet |
| Bromothymol blue | Yellow | Blue |
Chemical indicators are commonly used to test the acidic. basic nature of soils.
They are also used to test the acidic basic conditions of water in swimming pools and fish tanks.

The pH scale is a measure of how acidic or basic a chemical substance is.
- A pH of 7 is netural
- A pH less than 7 is acidic
- A pH greater than 7 is basic
| Strength | strong acids | weak acids | neutral | weak bases | strong bases |
| pH | 0-2 | 3-6 | 7 | 8-10 | 11-14 |
| Examples | Car acid batteries | Lemon juice | Water | Toothpaste | Oven cleaner |
Subscrever:
Comentários (Atom)